
Barrington, Illinois, 60010
United States
833-433-4626
www.dehnco.com Dehnco Company Profile


Organizing materials to coincide with the flow of the work creates efficiency.
Equipment, materials and supplies storage are always a workstation design issue. Organizing materials to coincide with the flow of the work creates efficiency.
If there is not enough storage area at the workstation, making the table larger is not necessarily the answer. In fact, the tabletop surface should not be considered storage space. When the work surface is cluttered with supplies, actual working space is reduced.
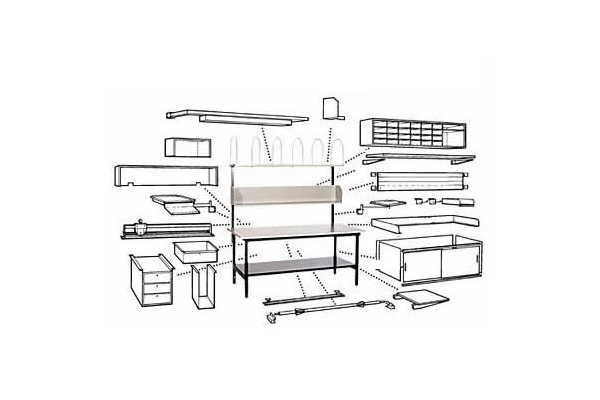
However, every workstation has potential for significant storage. Let’s look at a typical worktable.
There are 4 basic storage areas around a typical table.
The four storage areas are typically broken down into eight reach zones.
The four upper reach zones are areas accessible without bending and awkward movements. They are the zones that typically hold the most frequently used or most popular items and equipment.
The four lower reach zones are used more for bulk storage, larger items and slower moving materials. Access typically requires extra steps, bending and sometimes awkward reaches and movements.
The movement required to access a reach zone determines the “zone rating”.
Each of the four storage areas also has a lower reach zone. This space is typically not as efficient, since the worker has to step and bend to select material.
When workers move from their neutral position, they have to return to the neutral position. Therefore, the time used for every step is literally doubled. While these time increments seem minor, the accumulation of lost time can add up quickly if operations are inefficient.
In order to address the storage issue, it is necessary to compile a detailed list of equipment and supplies used at the workstation. The functional design of the worktable is directly related to the type and volume of supplies and equipment.
Create an equipment and supply bill of materials. Break the list into three parts.
Make sure the list is complete and detailed with number of items, flat box sizes, equipment dimensions and a complete list of supplies and related items. It is important to get an exact measurement on the volume of material.



